Tips / X-Wing
X-Wing
X-Wing is a simple “rectangle” pattern for eliminating candidates: focus on one digit d . If its candidate positions line up as the four corners of a rectangle, then the same digit outside the corners can be removed.
Starter
X-Wing
X-Wing is a simple “rectangle” pattern for eliminating candidates: focus on one digit d. If its candidate positions line up as the four corners of a rectangle, then the same digit outside the corners can be removed.
We use r1c1 to describe a cell position: r = row, c = column.
When can you use it?
Use this 3-step checklist:
- Pick a digit d
- Find two rows (or two columns) where d appears in exactly 2 candidate cells in each
- Those two pairs sit in the same two columns (or the same two rows)
⇒ you have the four corners of an X-Wing
Elimination rule: in those two columns (or rows), remove candidate d from every cell except the four corners.
One example (in two steps)
Step 1: Locate the four corners (image above)
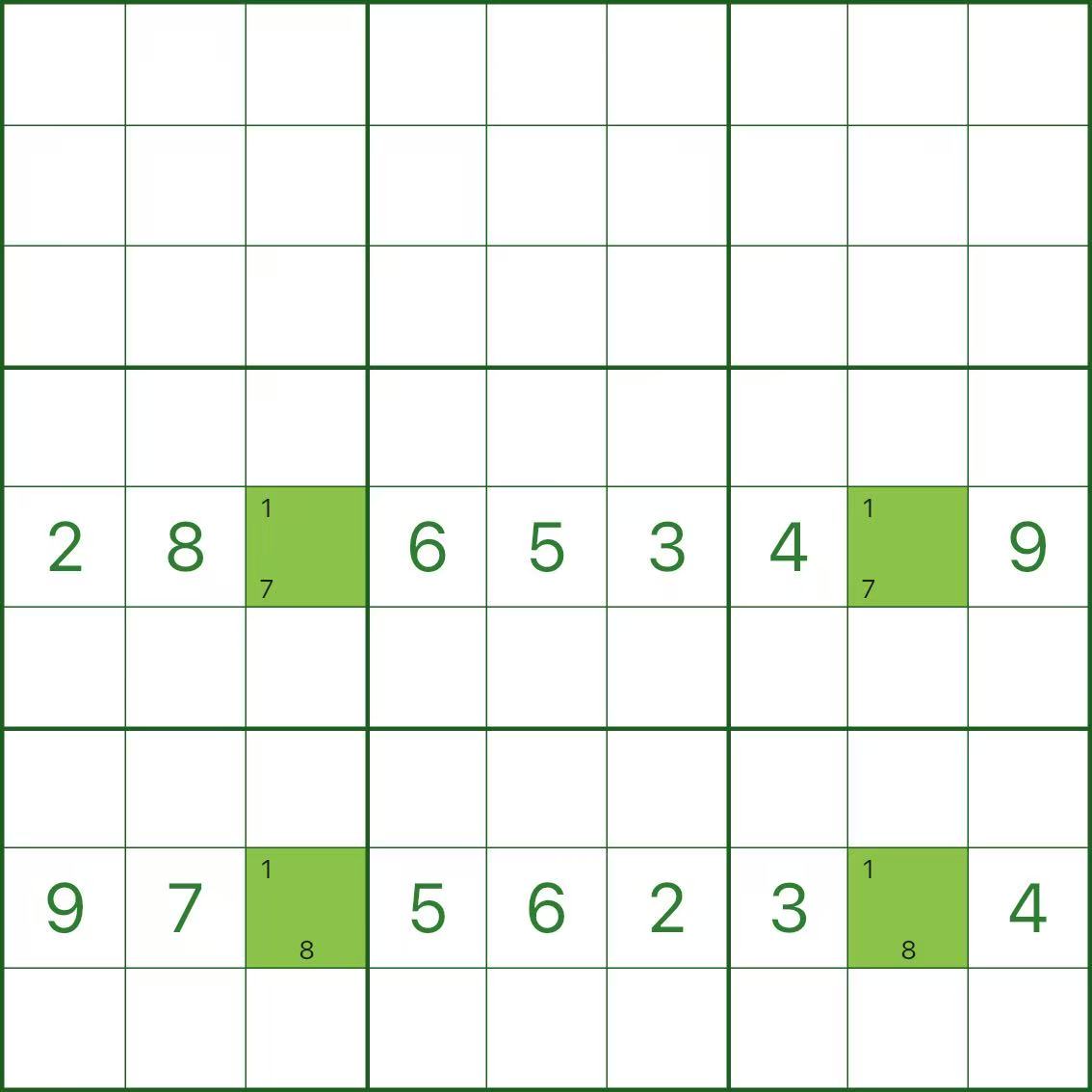
In the image above, we only show key information in row 5 and row 8.
Focus on r5c3, r5c8, r8c3, r8c8.
Even though those cells may also have other candidates, let’s only look at digit 1:
- On row 5, candidate 1 appears only in r5c3 or r5c8
- On row 8, candidate 1 appears only in r8c3 or r8c8
Most importantly, they share the same two columns (column 3 and column 8), forming a rectangle corner pattern.
Step 2: Why elimination works (image below)
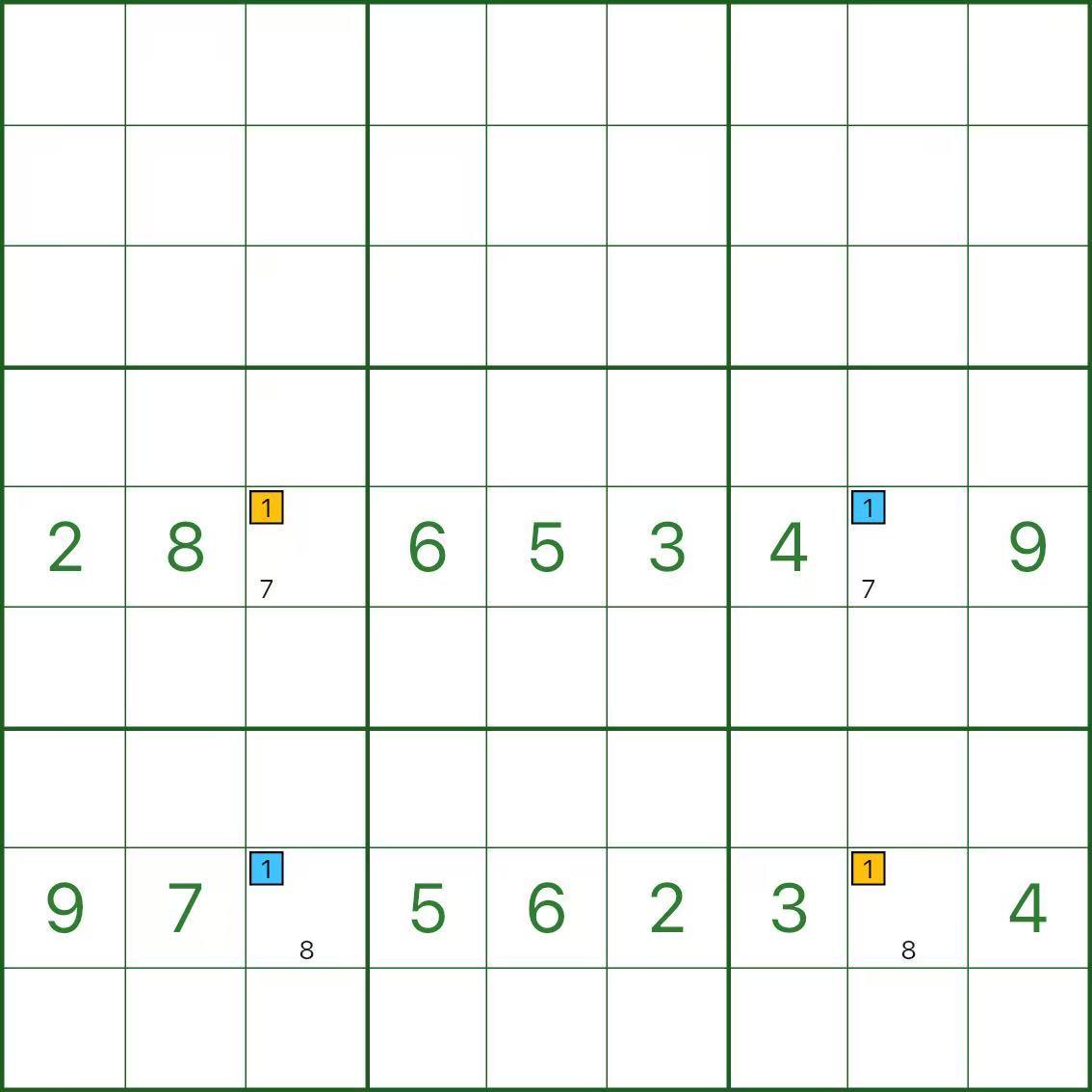
The key idea is very simple:
- On row 5, digit 1 can only be r5c3 or r5c8
- On row 8, digit 1 can only be r8c3 or r8c8
So in column 3 and column 8, digit 1 is “taken” by the rectangle corners (one in each row).
That’s why any other candidate 1 in those two columns is impossible and can be removed (the red candidates).
In a real puzzle
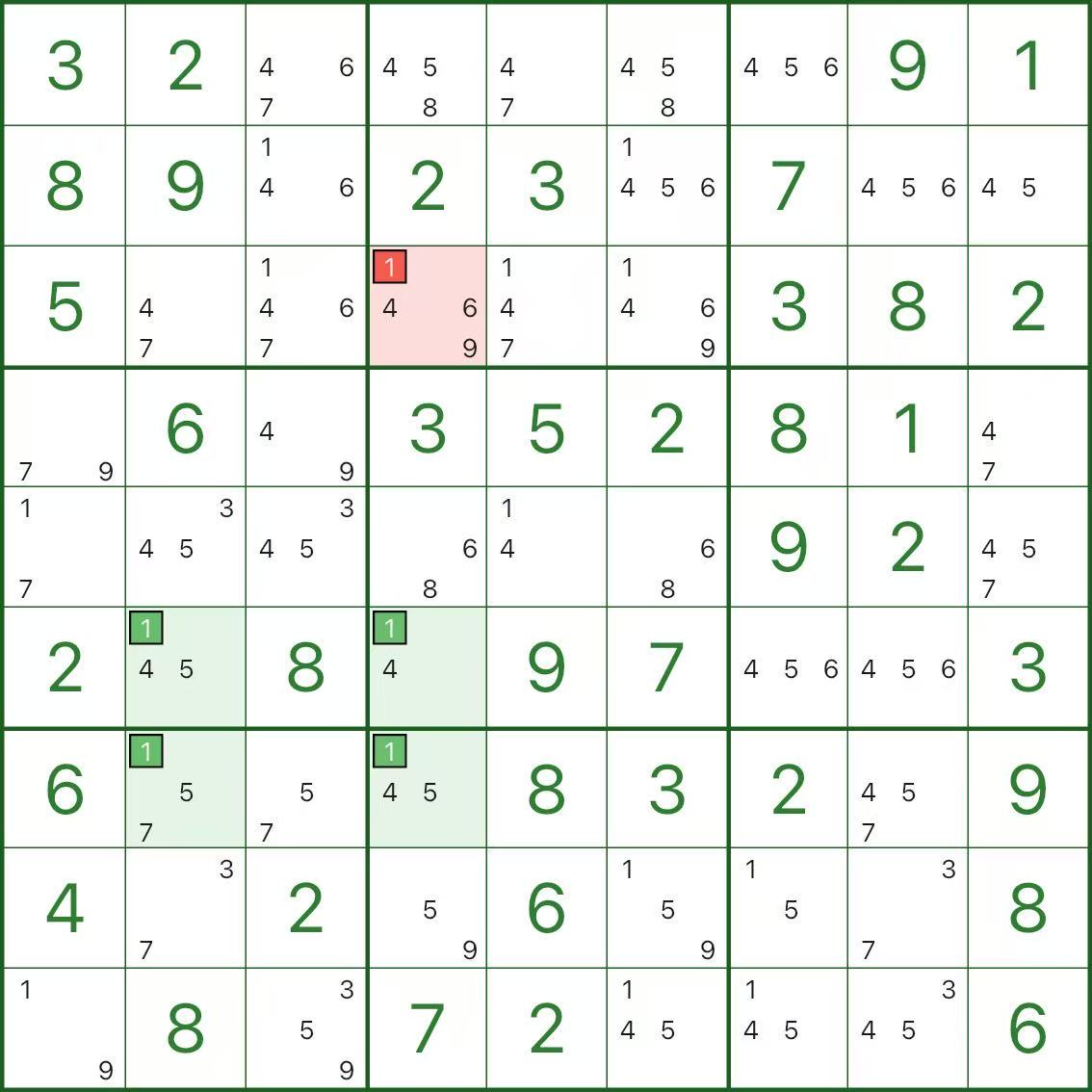
In the image above (a real puzzle screenshot), the green cells r6c2, r6c4, r7c2, r7c4 are the four corners for digit 1.
This is a “horizontal” X-Wing: rows 6 and 7 are the base, and the corners sit at the intersections with columns 2 and 4.
So in column 2 and column 4, any candidate 1 outside the corners can be removed — for example, the red candidate 1 in r3c4.
Summary
To spot an X-Wing quickly:
- Pick a digit d. Find two rows (or two columns) where d appears in exactly two candidate cells
- Those two rows (or columns) share the same two columns (or the same two rows), forming the rectangle corners
- Eliminate: remove d from the rest of those two columns (or rows), excluding the four corners