Tips / Skyscraper
Skyscraper
Prerequisite: Chain Basics
Intermediate
Skyscraper
Prerequisite: Chain Basics
Description
Skyscraper is a single-digit candidate elimination technique: focus on one digit d.
If digit d appears in exactly two candidate cells in each of two parallel rows/columns (two walls), and one endpoint from each wall lies on the same perpendicular row/column (the base), the other two endpoints are the roofs.
Any candidate d that can see both roofs can be eliminated.
Explanation
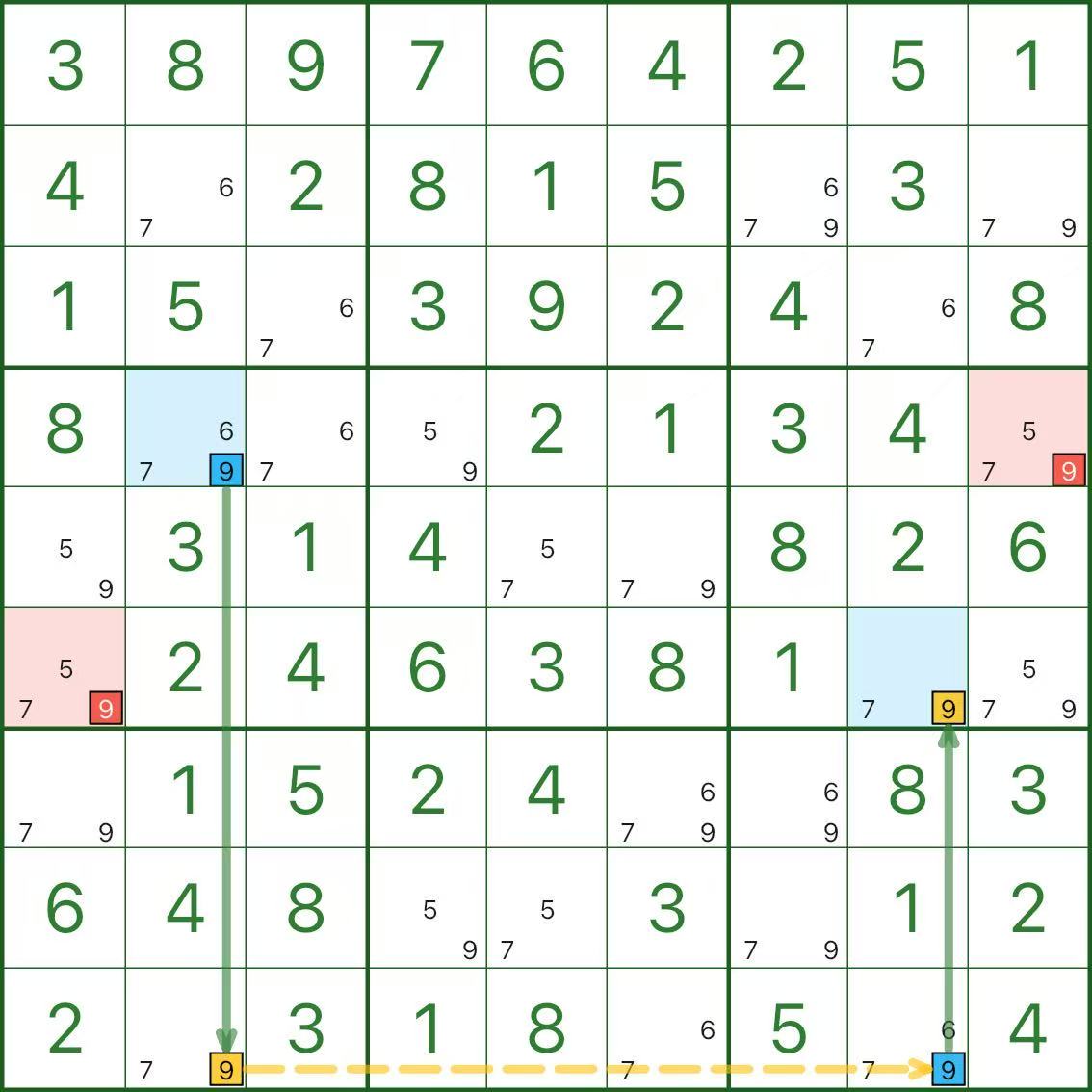
In the image above, the target digit is 9.
You can picture the pattern as a small “building”:
- Two walls (strong links): in column 2, digit 9 appears only in r4c2 and r9c2; in column 8, digit 9 appears only in r6c8 and r9c8
(exactly two spots in a unit ⇒ a strong link) - The base (weak link): the two “bottom” endpoints lie on row 9 (the yellow dashed line)
(a row can’t contain two 9s ⇒ they can’t both be true) - The roofs: the two top endpoints (the blue cells r4c2 and r6c8)
Now look at the red candidates: candidate 9 in r6c1 and candidate 9 in r4c9. Why can they be removed?
Here’s the short contradiction:
- Assume the red candidate 9 is true (use r6c1 as an example)
- It sees both roofs, so r4c2 ≠ 9 and r6c8 ≠ 9
- Each wall is a strong link, so 9 is forced onto the base endpoints r9c2 and r9c8
- But the base is one row, so it can’t contain two 9s → contradiction
Therefore, the red candidates can be eliminated.
Examples
The next two images show two different orientations. Use them as reference:
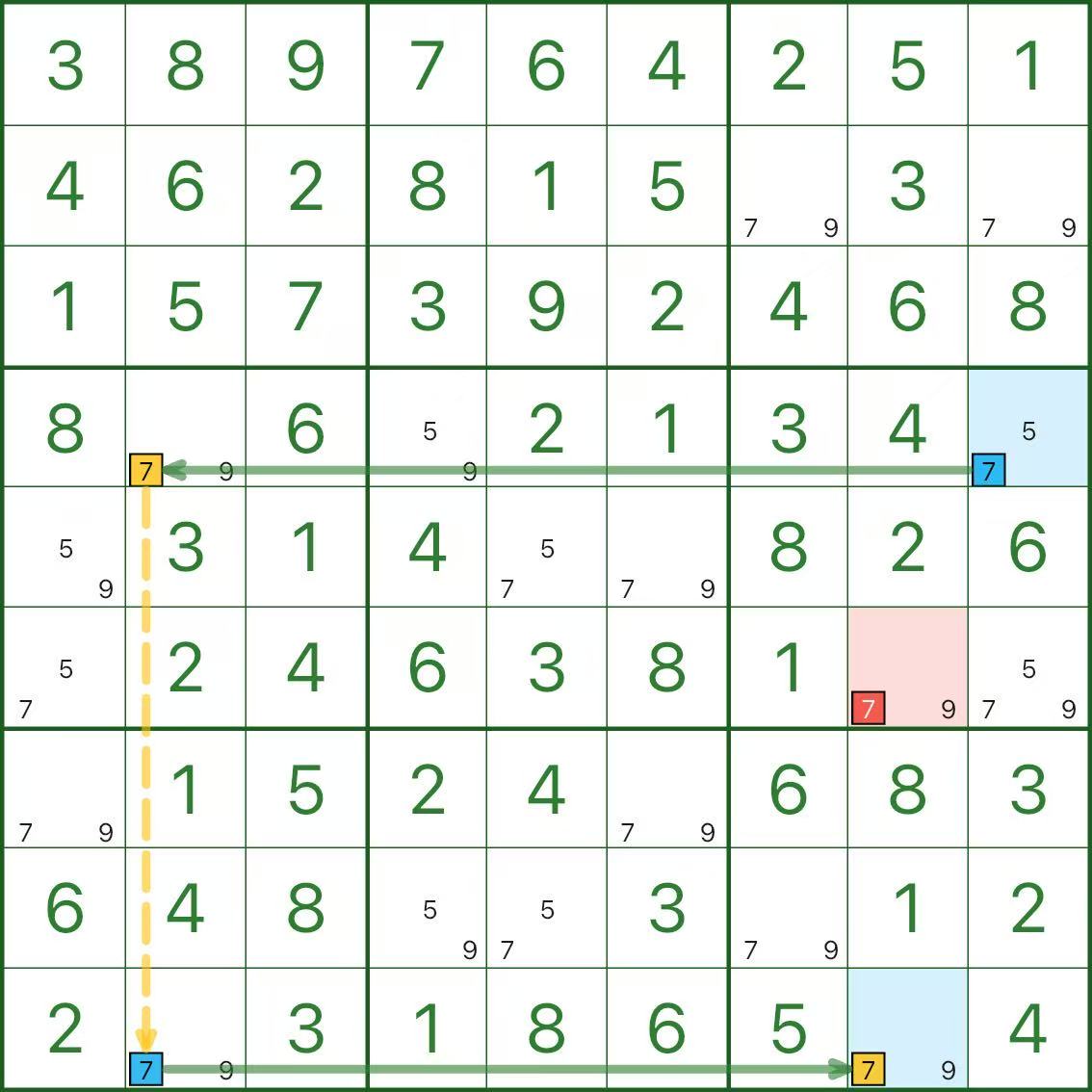
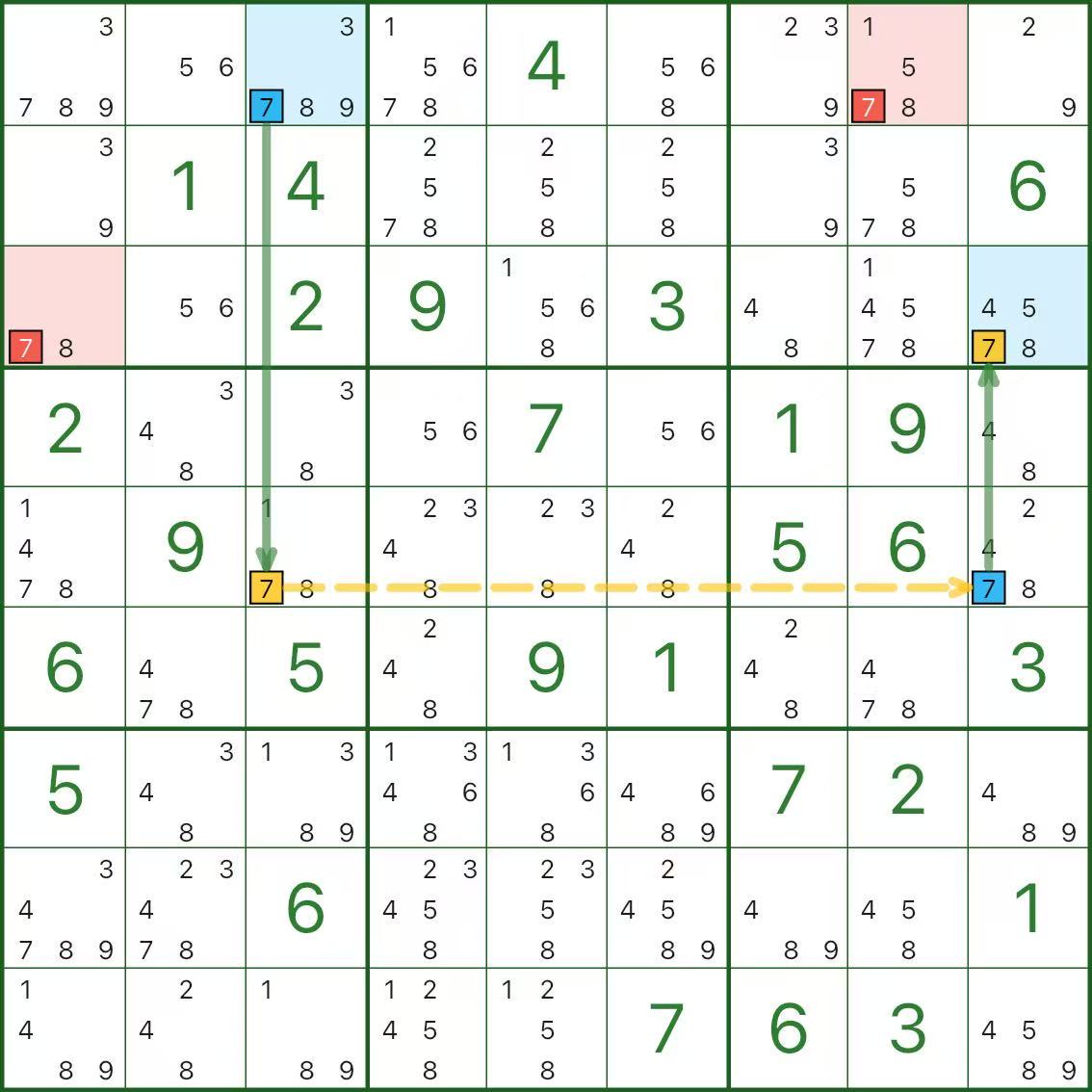
How to Find a Skyscraper
In a real puzzle, use this checklist:
- Pick a digit d
- Find two parallel rows/columns where digit d appears in exactly 2 candidate cells (two walls)
- Check whether one endpoint from each wall lies on the same perpendicular row/column (the base)
- The other endpoints are the roofs: candidates that can see both roofs are eliminations